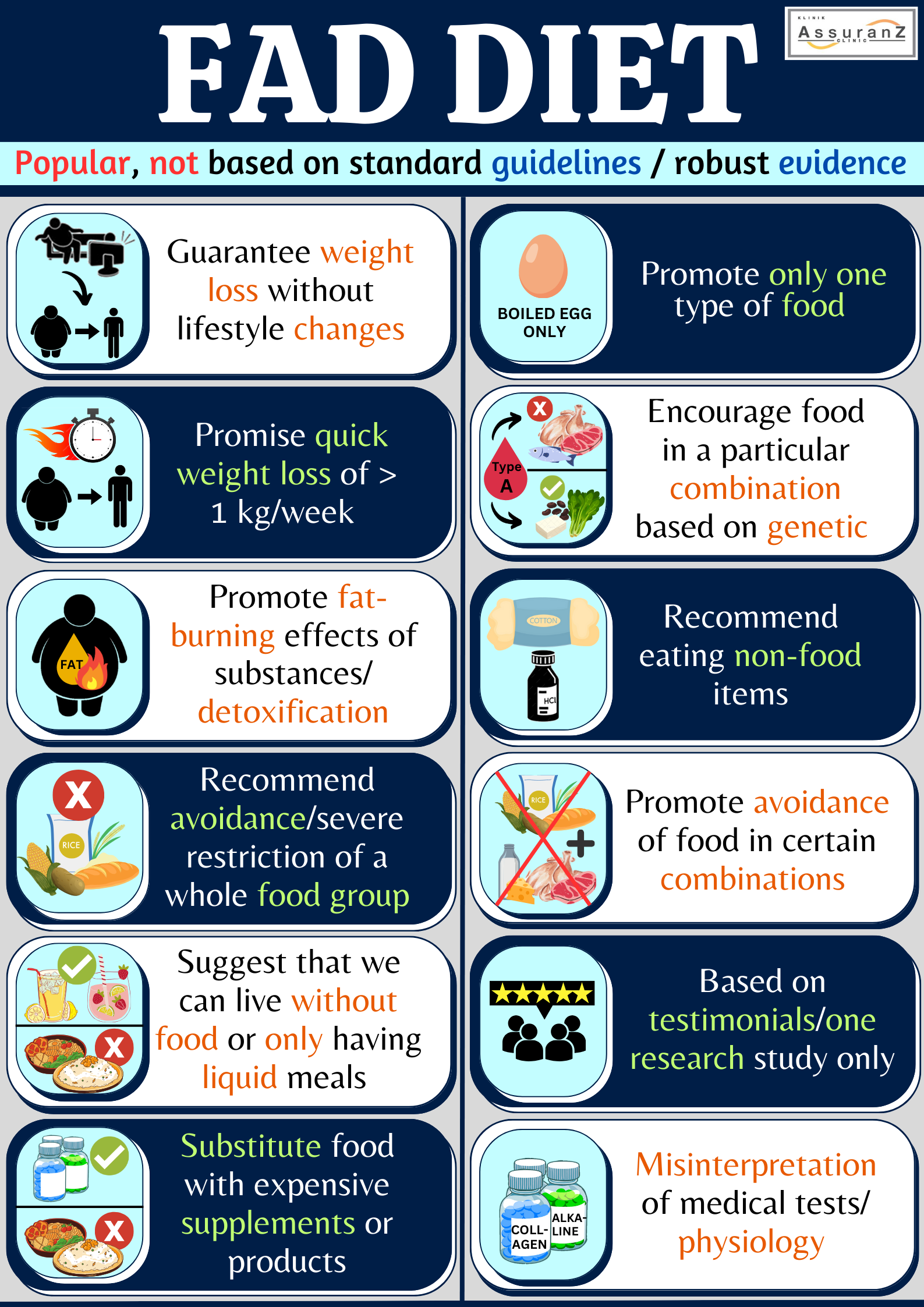
Fad diet refers to a variety of diets that are popular without being a standard dietary recommendation, with varying approaches and with no strong scientific evidence to support. These diets typically promise exaggerated short-term changes, or irrational health improvements. Beware of diets that are too good to be true. Some of the common characteristics of fad diets are:
食物盲从现象是指各种流行的饮食方式,但并不是标准的饮食推荐,方法各异,没有强有力的科学根据。这些饮食通常会带来夸大的短期变化或不合理的健康改善。谨防那些好得令人难以置信的饮食。食物盲从现象的一些共同特征是:
- Guaranteeing weight loss without needing to change our lifestyle in any way (for instance, diet pills or supplement, lotions, girdle et cetera).
保证减肥而不需要改变我们的生活方式(例如食用减肥药或补充剂、乳液、使用腰带等)。
- Promising quick weight loss of more than 1 kg of body fat weekly (such as very high fat and very low carbohydrate diet or extreme fasting).
保证每周快速减肥超过1公斤体脂(例如极高的脂肪和极低的碳水化合物或者极端禁食)。
- Promoting magical fat-burning effects of foods or substances (such as grapefruit diet, caffeine diet and green tea extract).
促进食物或物质的神奇脂肪燃烧效果(如柚子减肥法、咖啡因减肥法及绿茶萃取物)。
- Recommending avoidance or severe restriction of a whole food group such as all carbohydrates (<50 g carbohydrate per day except if medically prescribed), staple food or dairy products (in example, very low carbohydrate, palaeolithic, carnivore, general motor and cookie diets).
推荐避免或严格限制整个食物组,例如所有碳水化合物(一天少过50克碳水化合物,医疗处方除外)、主食或乳制品(例如极低的碳水化合物、旧石器时代饮食、肉食饮食、普通运动饮食和饼干饮食)。
- Suggesting that we can survive without food or by only having liquid meals (for instance, water fasting, master cleanse or juice cleanse).
表明我们可以在没有食物的情况下生存或者只吃流食(例如清水断食、枫糖柠檬断食法或果汁排毒)。
- Suggesting substitution of everyday foods for expensive supplement doses, ingredients, or special products (such as weight loss injection and the bulletproof diet).
建议使用日常食物替代昂贵的补充剂剂量、成分或特殊产品(例如减肥注射剂和防弹饮食)。
- Promoting only one type of food (mono diet, for example cabbage soup diet and boiled egg diet) or avoiding all cooked food (raw food diet).
只提倡一种食物(单一食物,如白菜饮食和水煮蛋饮食)或避免所有熟食(生食饮食)。
- Encouraging consumption of foods only in a particular combination based on genetic type (blood group diet).
鼓励仅食用基于基因类型的的特定组合的食物(血型饮食)。
- Promoting ‘detoxification’ or avoiding food in certain combinations (such as separating the consumption of carbohydrate and protein, the fat flush diet, master cleanse et cetera).
推动“排毒”或避免某些组合的食物(例如分开摄入碳水化合物和蛋白质、消脂饮食法、枫糖柠檬断食法等)。
- Recommending eating non-food items such as hydrochloric acid and cotton wool.
推荐食用非食物物品,如盐酸和脱脂棉。
- Wrong application or misinterpretation of medical tests or human physiology (such as alkaline diet and collagen diet).
医学测试或人体生理学的错误应用或误解(例如碱性饮食和胶原蛋白饮食)。
- Diet based on testimonials or one research study only.
仅一项研究或仅推荐的饮食。
A lot of these diets can generate initial weight loss, but it is often due to lean muscle and fluid loss instead of body fat. These diets are also typically rigid and difficult to follow in long term, can lead to cycles of weight loss and weight regain, and negatively affect our relationship with food. They are also likely to cause malnutrition as the diet composition is not balanced. Other side effects include dehydration, fatigue, constipation, headache, nausea, and vomiting.
许多这样的饮食一开始可以使体重减轻,但这通常是瘦肌肉和液体的流失,而不是体内脂肪的减少。这些饮食通常也很严格,难以长期遵循,可能导致体重减轻和体重反弹的循环,并对我们与食物的关系产生负面影响。由于饮食结构不均衡,它们还可能导致营养不良。其他副作用包括脱水、疲劳、便秘、头痛、恶心和呕吐。
Diets that qualify as fad can change based on time, social, cultural, and subjective views. Some diets, though are included in these categories, might be used in medical settings based on therapeutic indications such as liquid diet for dysphagia (difficulty to swallow) or post-operation, very low-calorie diet for pre-bariatric surgery, and Ketogenic or Atkins diet (very low carbohydrate diet) for epilepsy. However, the use of these diets should be under supervision of healthcare professionals.
符合时尚的饮食可以根据时间、社会、文化和主观观点而改变。有些饮食虽然包含在这些类别中,但可能会在医疗环境中根据治疗适应症使用,例如治疗吞咽困难的流质饮食或手术后用于减肥手术前的极低热量饮食,以及治疗癫痫的生酮或阿特金斯饮食(极低碳水化合物饮食)。然而,这些饮食的使用应在医疗保健专业人员的监督下进行。
Overall, there is no ‘one type fit for all’ diet as individuals differ metabolically, physically, and genetically. However, diets that can lead to malnutrition are certainly not recommended. For the general population, stick to the guidelines provided by the Ministry of Health (i.e. Quarter-quarter-half plate) as they are easy to follow and are balanced. For those with medical conditions such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, kidney disease et cetera, special care is needed, therefore, it is suggested for you to refer to the healthcare professionals to determine the type of diet suitable for you.
总体而言,不存在“一种适合所有人”的饮食方式,因为个体在代谢、身体和遗传上存在差异。然而,肯定不会推荐可能导致营养不良的饮食。对于一般人群,请遵循卫生部提供的指南(即健康餐盘),因为它们易于遵循且均衡。对于患有肥胖、糖尿病、高血压、肾病等疾病的人士来说,需要特别照顾,因此建议您咨询医护人员以确定适合您的饮食类型。