THE KETOGENIC DIET / 生酮饮食
The ketogenic diet (keto diet) is a high fat and low carbohydrate intake used as a treatment of refractory epilepsy, reduction of body weight, body fat, and to improve metabolic health. This diet instigates ketosis, where the body fat is used as the primary energy source instead of carbohydrates. Keto diet generally has a macronutrient distribution of 55 to 60% fat with some type up to 80%, 10 – 35% protein and 5 to 10% carbohydrate (20 to 50 g/day). Depending on the aim of keto diet, whether it is used to treat epilepsy or for weight reduction, energy and fluid restrictions may or may not be required.
生酮饮食(keto Diet)是一种高脂肪和低碳水化合物的摄入方式,用于治疗难治性癫痫、减少体重、体脂以及改善代谢健康。这种饮食会引发酮症,即身体脂肪代替碳水化合物作为主要能量来源。生酮饮食的常量营养素分布通常为55%至60%脂肪,某些类型高达80%、10至35% 蛋白质和5至10% 碳水化合物(20至50克/天)。根据生酮饮食的目的,无论是用于治疗癫痫还是用于减肥,可能需要也可能不需要限制能量和液体。
PROS / 优点
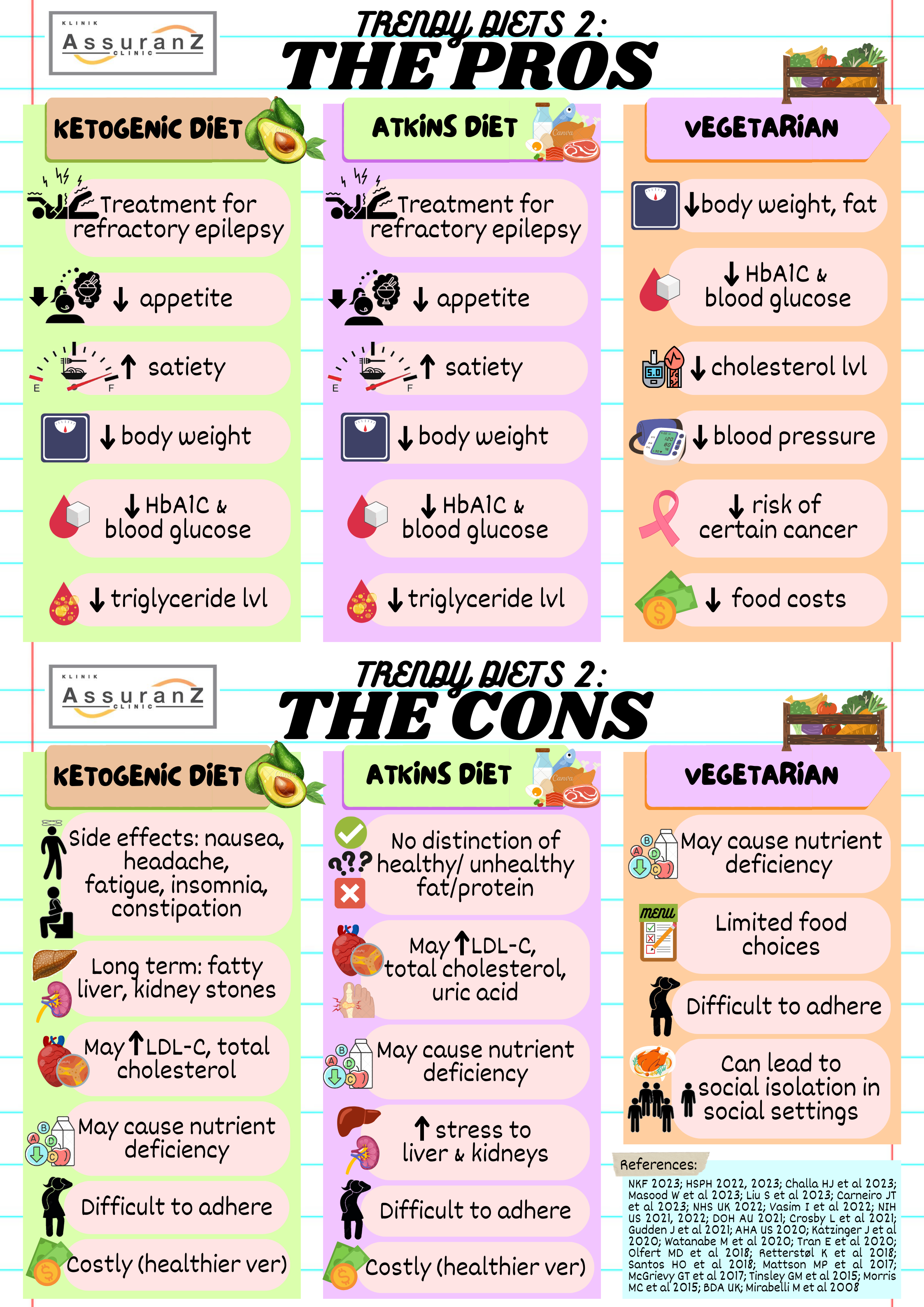
- A treatment of refractory epilepsy – possibly by reducing excitability of neuron.
难治性癫痫的治疗 – 可能通过降低神经元的兴奋性来治疗。
- Can suppress appetite and increase satiety, leading to reduced calorie intake and subsequently, weight loss.
可以抑制食欲并增加饱腹感,来减少热量摄入,从而减轻体重。
- Can cause reduction of HbA1c (average 3 months blood sugar level) and blood glucose level due to carbohydrate restriction.
由于限制碳水化合物的摄入,可能导致HbA1c(平均3个月血糖水平)和血糖水平的降低。
- Might lead to reduction of triglycerides due to calorie reduction as the body reduce energy storage in the form of triglycerides.
由于身体减少三酸甘油酯形式的能量储存,热量减少可能导致三酸甘油酯的减少。
CONS / 缺点
- Short term side effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, insomnia, fatigue, reduced exercise tolerance and constipation.
短期副作用包括恶心、呕吐、头痛、头晕、失眠、疲劳、运动耐量降低和便秘。
- May cause long term side effects including hepatic steatosis (fatty liver), low protein in blood, kidney stones, and vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
可能造成长期副作用包括肝脂肪变性(脂肪肝)、血液中蛋白质含量低、肾结石以及维生素和矿物质的缺乏。
- May increase total cholesterol, LDL-C and VLDL-C levels from high saturated fat and low fibre intake, thus increasing risk of cardiovascular diseases.
高饱和脂肪和低纤维摄入量可能会增加总胆固醇、低脂胆固醇(LDL-C)和极度低脂胆固醇(VLDL-C)水平,从而增加患心血管疾病的风险。
- May lead to nutritional deficiencies due to lack of vitamins (typically thiamine, folate, vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin K and vitamin B6), minerals (calcium, magnesium, iron, and potassium), fibre and phytochemical from vegetables, fruits, and wholegrains.
由于缺乏维生素(通常是硫胺素、叶酸、维生素A、维生素E、维生素K和维生素B6)、矿物质(钙、镁、铁和钾)、蔬菜、水果及全谷物里的纤维和植物化学物质,可能会导致缺乏营养。
- Not suitable for people with certain medical condition (for instance, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes).
不适合患有某些疾病的人(例如高胆固醇和糖尿病患者)。
- Difficult to maintain due to strict restriction of staple food.
主食严格限制,很难维持。
- Can be expensive with healthier version of the diet.
更健康的饮食导致价格可能更昂贵。
THE ATKINS DIET / 阿特金斯饮食法
The traditional Atkins diet is a high-protein, high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet developed for weight loss. It is a subtype of ketogenic diet. Similar to keto diet, this diet induces ketosis state, so that the body will burn fat instead of carbohydrate to use as the main energy source. The Atkins diet is done by stages, which are, 1) Induction phase where individuals restrict carbohydrates to 20 g/day, excluding fibre and sugar alcohols to induce ketosis; 2) Ongoing weight-loss phase where carbohydrates are slowly increased at a rate of 5 g/week up to 25 to 50 g/day by slowly introducing nuts, low-carbohydrate vegetables, fruits and dairy; 3) Pre-maintenance phase where one will raise daily carbohydrate intake in 5 to 10 g/day increment up to 80 g/day. Phase 3 will last until individual has lost the target amount of weight and is able to keep it for a full month; 4) Maintenance phase is when a goal of carbohydrate level of 40 to 90 g/day is entered to maintain weight loss – perhaps for the rest of the lives. There is no restriction of fat and protein, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and most cheeses.
传统的阿特金斯饮食法是为减肥而开发的高蛋白、高脂肪、低碳水化合物饮食法。它是生酮饮食的一个亚型。与生酮饮食类似,这种饮食会诱发酮症状态,使身体燃烧脂肪而不是碳水化合物作为主要能量来源。阿特金斯饮食是分阶段进行的,即:
1)诱导阶段,个人将碳水化合物限制在20克/天,排除纤维和糖醇以诱导酮症
2) 持续减肥阶段,通过缓慢引入坚果、低碳水化合物蔬菜、水果和乳制品,以每周5克的速度缓慢增加碳水化合物,直至每天25至50克
3) 维持前阶段,每日碳水化合物摄入量以5至10克/天的增量增加至80克/天。第三阶段将持续到个人减掉目标体重并能够保持一个月
4) 维持阶段是指进入每天40至90克碳水化合物水平的目标,以维持减肥效果——也许终生如此。脂肪和蛋白质没有限制,包括肉类、家禽、鱼类、鸡蛋和大多数奶酪。
PRO / 优点
- A less strict, more tolerable treatment of refractory epilepsy in comparison to keto diet.
与生酮饮食相比,它的耐受性更好,难治性癫痫的治疗不那么严重。
- Similar to keto diet, can suppress appetite and increase satiety, leading to reduced calorie intake and subsequently, weight loss.
与生酮饮食类似,它可以抑制食欲并增加饱腹感,减少卡路里的摄入,从而减轻体重。
- Can cause reduction of HbA1c and blood glucose level due to reduction of carbohydrate intake.
碳水化合物摄入量少,可能会导致平均3个月血糖水平(HbA1c)和血糖水平降低。
- Can reduce triglyceride due to calorie reduction.
卡路里的减少可以降低三酸甘油酯。
CONS / 缺点
- Lack of differentiation between healthy and unhealthy high-protein/high-fat foods (such as saturated and trans-fat).
缺乏区分健康与不健康的高蛋白/高脂肪食品(例如饱和脂肪和反式脂肪)。
- May cause increase of total cholesterol and LDL-C due to high consumption of animal products containing saturated fat.
大量食用含有饱和脂肪的动物产品,可能导致总胆固醇和低脂胆固醇升高。
- May cause uric acid increment as animal protein is rich in purine, and purine’s byproduct of metabolism is uric acid.
可能导致尿酸升高,因为动物蛋白富含嘌呤,而飘零代谢的产物就是尿酸。
- Like keto diet, may lead to nutritional deficiencies due to lack of vitamins, minerals, fibre and phytochemical from vegetables, fruits, and wholegrains.
与生酮饮食一样,缺乏蔬菜、水果和全谷物的维生素、矿物质、纤维和植物化学物质,可能会导致缺乏营养。
- Can increase stress on the liver and kidneys, thus not recommended for people with impaired kidney and liver function as it will lead to worsening of the disease.
会增加肝脏和肾脏的压力,因此不建议患有肾脏和肝脏功能受损的人使用,因为会导致病情恶化。
- Difficult to maintain due to strict restriction of staple food.
主食严格限制,很难维持。
- Can be expensive with healthier version of the diet.
更健康的饮食导致价格可能更昂贵。
THE VEGETARIAN DIET / 素食
Vegetarian generally refers to plant-based diet. However, there are a few types of vegetarian diets practiced by individuals depending on various factors such as health, environment, ethical, religious, and economic reasons. The types of vegetarianism are 1) vegan, referring to people who avoid all animal based foods including animal by-products such as gelatine, 2) lacto-ovo-vegetarian which refers to people who do not consume meat and seafood but do take dairy products and eggs, 3) lacto-vegetarian where individuals do not eat meat, seafood and eggs but include dairy foods, 4) ovo-vegetarian where people consume eggs but do not include meat, seafood and dairy products in their diet. Other diets that are not strictly vegetarian but still focus on limiting animal products are 1) pescetarian where individuals consume seafood, dairy and eggs but not meat and 2) flexitarian (also known as semi-vegetarian) where ones stick to plant-based diet mainly but do consume small portions of meat and seafood sometimes. Those practicing pescetarian or flexitarian normally do so to obtain the health benefits of eating a largely vegetarian diet without needing to give up meat entirely.
素食一般是指以植物为主的饮食。然而,根据健康、环境、道德、宗教和经济原因等多种因素,个人实行的素食有几种类型。素食主义的类型是:
1) 素食主义者:指避免所有动物性食品的人,包括动物副产品,如明胶
2) 乳蛋素食者:指不食用肉类和海鲜但食用乳制品和鸡蛋的人
3) 乳素食:即不吃肉、海鲜和鸡蛋,但包括乳制品的人
4) 蛋素食:即食用鸡蛋,但饮食中不包括肉、海鲜和乳制品的人。
其他并非严格素食但仍注重限制动物产品的饮食包括:
1) 鱼素饮食:即食用海鲜、乳制品和鸡蛋,但不食用肉类的人
2) 弹性素食(也称为半素食):即主要坚持植物性饮食但有时也会吃少量的肉类和海鲜。那些实行鱼素素食或弹性素食的人通常这样做是为了获得主要素食的健康益处,而无需完全放弃肉类。
Pros / 优点
- Can aid in weight loss, body fat loss and is protective against weight gain associated with lower intake of energy and total fat.
有助于减肥、减少体脂肪,并防止因能量和总脂肪摄入量减少而导致的体重增加。
- Reduce risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, stroke et cetera due to lower intake of saturated fat and cholesterol.
饱和脂肪和胆固醇的摄入量低,可以降低患上心脏病、中风等心血管疾病的风险。
- Reduce risk of diabetes with reduction of HbA1c level associated with high fibre intake and anti-inflammatory food (polyphenols and antioxidant).
通过高纤维的摄入及抗炎食物(多酚和抗氧化剂)来降低HbA1c(平均3个月血糖水平),从而降低糖尿病风险。
- Reduce risk of hypertension due to high potassium, polyphenols and vitamin C, and low sodium consumption (natural sodium from animal, or from cured and processed meat).
含高钾、多酚、维生素C和低钠的消耗(来自动物或腌制及加工肉类的天然钠),可降低高血压的风险。
- Reduce risk of certain cancer types with lower consumption of processed and red meat, and high fibre and antioxidant consumption.
通过减少加工肉类和红肉的摄入量,高纤维和抗氧化食物的摄入量来降低某些类型的癌症风险。
- Reduce food costs.
降低食品成本。
Cons / 缺点
- May lead to nutrient deficiency, most commonly protein, vitamin B12, omega-3 fatty acid, vitamin D, calcium and iron leading to diseases such as anaemia, brittle bone, and muscle weakness.
可能导致营养缺乏,最常见的是蛋白质、维生素B12、Omega-3脂肪酸、维生素D、钙和铁,从而导致贫血、骨骼疏松症和肌肉无力等。
- Limited food choices, causing difficulty to adhere to diet.
有限的食物选择,导致难以坚持饮食。
- Can lead to social isolation due to inconveniences in social settings such as limited dining out option and food choices during events.
社交环境的不便,如外出就餐和活动期间有限的食物选择,可能会导致社交孤立。